IoT Based Smart Agriculture Application Solution Circuit Diagram Increased Yield: By optimizing farming practices, IoT-based systems often result in higher crop yields and improved crop quality (Kumar & Singh, 2016). Real-World Impact: The implementation of IoT-based crop monitoring systems is not confined to theory; it has already made a significant impact in agriculture worldwide. Farmers are reporting This paper explores IoT-based Smart Farming technology, as well as Machine Learning-based plant disease detection. This technology decreases farmers and growers physical labor, increasing output in every way conceivable. Wireless sensors, cloud computing, communication technologies and various machine learning algorithms are all discussed Hence the method is making agriculture smart using automation and IoT technologies. Internet of Things (IoT) enables various applications of crop growth monitoring and selection, automatic irrigation decision support, etc. We proposed ESP8266 IoT Automatic irrigation system to modernize and improve the productivity of the crop.
As the population grows and the quality of life of the people improves, leading to heightened demand for salubrious food. As a result, indoor farming has become a very popular day by day and the By monitoring and managing the temperature, humidity, light, and CO2 in the polyhouse, a grower may maximise crop quality, production and minimising impact of environmental factors such as climate, rainfall etc. IoT-based polyhouse farming systems are incredibly simple to use and can be accessed from any location using a smartphone, tablet, or

IoT Based Polyhouse Farming with Controlled Environment and Monitoring Circuit Diagram
IoT (Internet of Things) is one of the most powerful things that allow us to control and monitor crops and plants over the internet. In this tutorial, we will learn how to make a smart agriculture system using ESP 32/NodeMCU. Our project will help us monitor the soil moisture of the plants or crops over the internet. Requirements
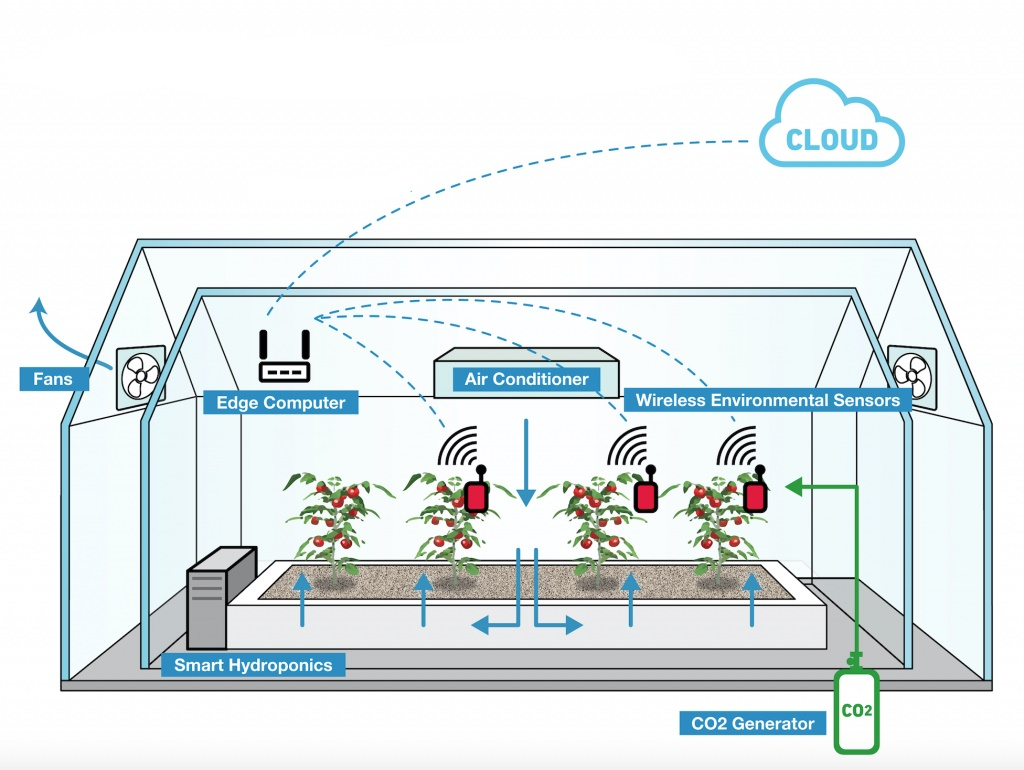
IoT solutions for farming aim to reduce output losses and meet rising demand from traditional farming operations. IoT in agriculture uses robots, drones, remote sensors and computer imaging. Wireless temperature and humidity sensors adjust ventilation and shading. Remote-controlled irrigation and lighting systems reduce manual labor. Cloud-based monitoring allows farmers to manage greenhouse conditions from anywhere. 5. Drone-Based Precision Farming . Drones equipped with high-resolution cameras and wireless connectivity improve

